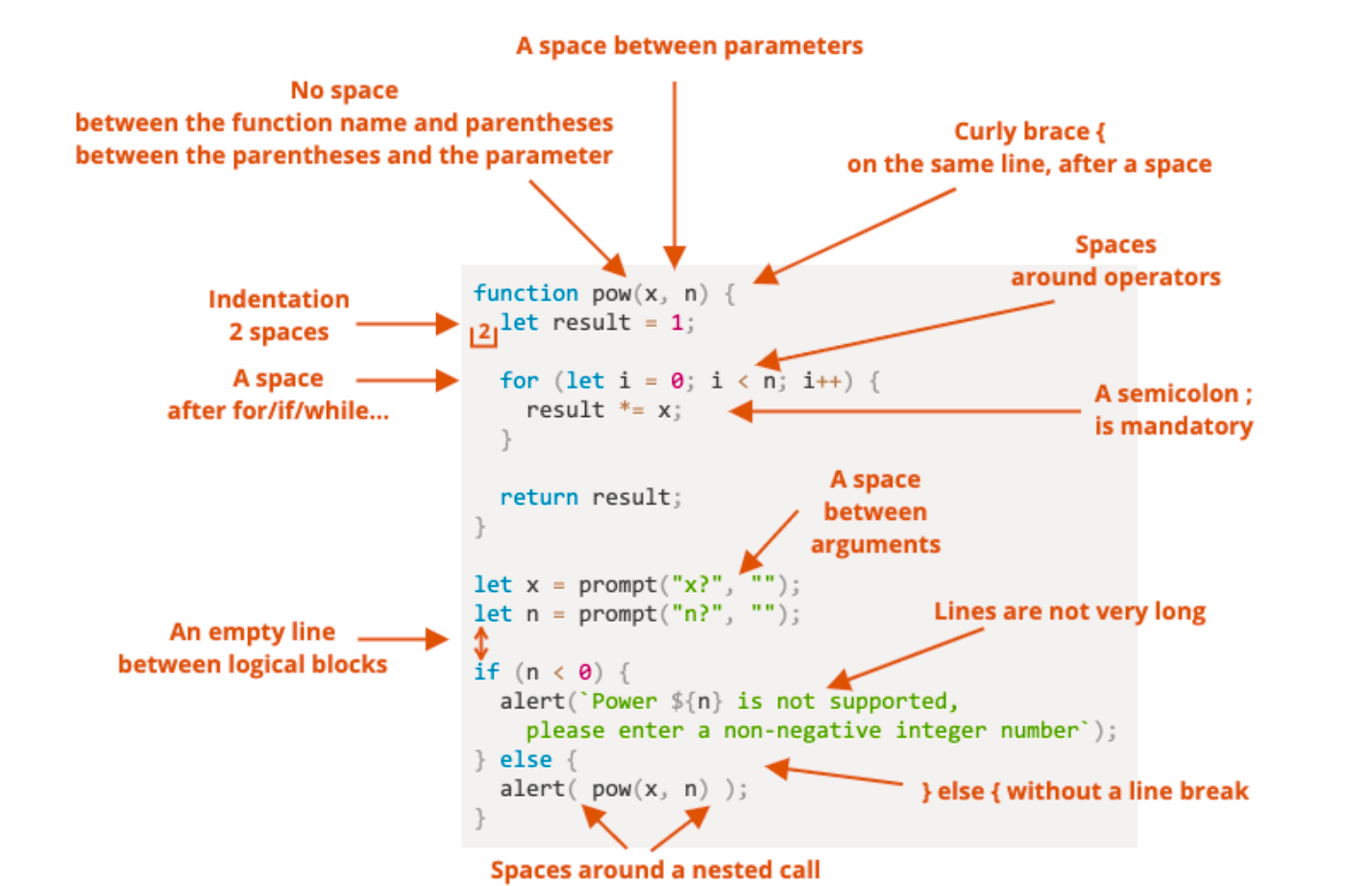
代码风格
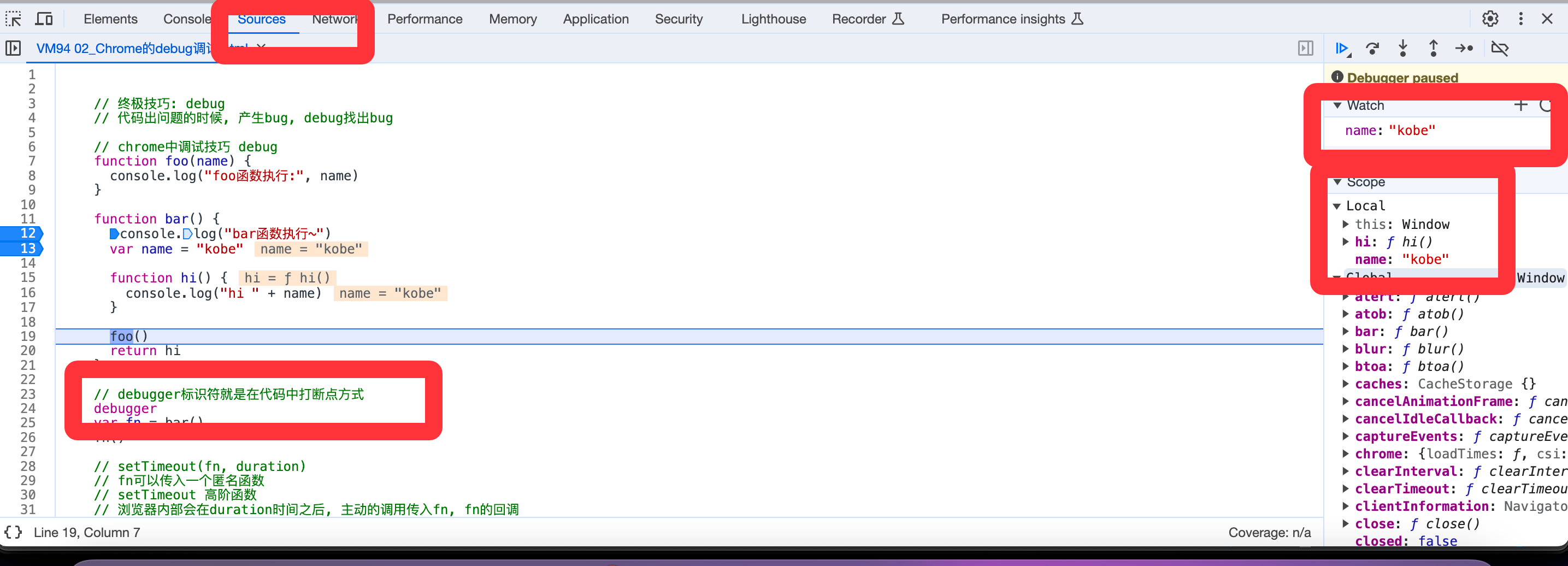
代码调试
面向对象
创建对象
1 // 一系列的学生对象
2 // 重复代码的复用: for/函数
3 var stu1 = {
4 name: "why",
5 age: 18,
6 height: 1.88,
7 running: function() {
8 console.log("running~")
9 }
10 }
11 var stu2 = {
12 name: "kobe",
13 age: 30,
14 height: 1.98,
15 running: function() {
16 console.log("running~")
17 }
18 }
19 var stu3 = {
20 name: "james",
21 age: 25,
22 height: 2.05,
23 running: function() {
24 console.log("running~")
25 }
26 }
1
2 // 工厂函数(工厂生产student对象) -> 一种设计模式
3 // 通过工厂设计模式, 自己来定义了一个这样的函数
4 function createStudent(name, age, height) {
5 var stu = {}
6 stu.name = name
7 stu.age = age
8 stu.height = height
9 stu.running = function() {
10 console.log("running~")
11 }
12 return stu
13 }
14
15 var stu1 = createStudent("why", 18, 1.88)
16 var stu2 = createStudent("kobe", 30, 1.98)
17 var stu3 = createStudent("james", 25, 2.05)
18 console.log(stu1)
19 console.log(stu2)
20 console.log(stu3)
1 // JavaScript已经默认提供给了我们可以更加符合JavaScript思维方式(面向对象的思维方式)的一种创建对象的规则
2 // 在函数中的this一般指向某一个对象
3 /*
4 如果一个函数被new操作符调用
5 1.创建出来一个新的空对象
6 2.让this指向这个空对象
7 3.执行函数体的代码块
8 4.如果没有明确的返回一个非空对象, 那么this指向的对象会自动返回
9 */
10 function coder(name, age, height) {
11 this.name = name
12 this.age = age
13 this.height = height
14 this.running = function() {
15 console.log("running~")
16 }
17 }
18
19 // 在函数调用的前面加 new 关键字(操作符)
20 var stu1 = new coder("why", 18, 1.88)
21 var stu2 = new coder("kobe", 30, 1.98)
22 console.log(stu1, stu2)
内存分配
原始类型占据的空间是在栈内存中分配的;
对象类型占据的空间是在堆内存中分配的;
原始类型的保存方式:在变量中保存的是值本身
所以原始类型也被称之为值类型;
对象类型的保存方式:在变量中保存的是对象的“引用”
所以对象类型也被称之为引用类型;
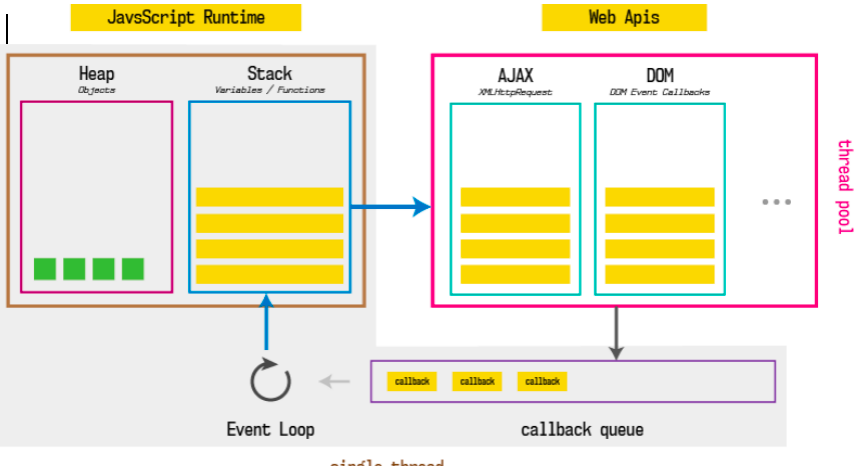
this
以默认的方式调用一个函数,this指向window;
通过对象调用,this指向调用的对象;
构造函数
JavaScript中的构造函数是怎么样的?
构造函数也是一个普通的函数,从表现形式来说,和千千万万个普通的函数没有任何区别;
那么如果这么一个普通的函数被使用new操作符来调用了,那么这个函数就称之为是一个构造函数;
1
2 // 创建一系列的对象
3 // 构造函数的名称: 使用大驼峰
4 function Person() {
5
6 }
7 var p1 = new Person()
8 console.log(p1)
9
10 // 平时创建普通的对象
11 // new Object()
12 var obj1 = {}
13 var obj2 = new Object()
14 var obj3 = new Person()
函数也是对象
function 继承 Object
1 function sayHello() {
2 }
3 sayHello.age = 18
4 console.log(sayHello.age)
内置类型
原始类型、包装类型
JavaScript的原始类型并非对象类型,所以从理论上来说,它们是没有办法获取属性或者调用方法的。
1var message = "hello world"
2var words = message.split("")
3var len = messages.length
4
5
6// 其实是 js引擎会干这些事情
7var message = new String("hello world")
原始类型是简单的值,默认并不能调用属性和方法;
这是因为JavaScript为了可以使其可以获取属性和调用方法,对其封装了对应的包装类型;
常见的包装类型有:String、Number、Boolean、Symbol、BigInt类型
Number类型
number 它有一个对应的数字包装类型Number
1 // Number构造函数 -> window.Number
2 // var num = 123 // new Number(num)
3
4 // 类属性
5 // Number中本身是有自己的属性
6 console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE)
7 console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE)
8 // integer: 整数
9 console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
10 console.log(Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER)
11
12 // 对象的方法
13 // toString(base)
14 var num = 1000
15 console.log(num.toString(), typeof num.toString())
16 console.log(num.toString(2))
17 console.log(num.toString(8))
18 console.log(num.toString(16))
19
20 // console.log(123..toString(2))
21
22 // toFixed的使用(重要)
23 var pi = 3.1415926
24 console.log(pi.toFixed(3))
25
26 // 类的方法
27 // parseInt
28 // parseFloat
29 // 整数: 123
30 // 浮点数: 小数 123.321
31 var num1 = "123.521"
32 console.log(Number(num1).toFixed(0))
33 console.log(Number.parseInt(num1))
34 console.log(Number.parseFloat(num1))
35
36 // window对象上面
37 console.log(parseInt(num1))
38 console.log(parseFloat(num1))
39
40 // function HYNumber() {
41 // }
42 // HYNumber.parseInt2 = function() {
43 // }
44 // window.parseInt2 = HYNumber.parseInt2
45 // console.log(window.parseInt2 === HYNumber.parseInt2)
46
47 console.log(parseInt === Number.parseInt)
Math对象
Math是一个内置对象(不是一个构造函数),它拥有一些数学常数属性和数学函数方法;
Math常见的方法:
- Math.floor:向下舍入取整
- Math.ceil:向上舍入取整
- Math.round:四舍五入取整
- Math.random:生成0~1的随机数(包含0,不包含1) Math.pow(x, y):返回x的y次幂
Math中还有很多其他数学相关的方法,可以查看MDN文档:
1 // console.log(typeof Number) // function
2 // var num = new Number()
3
4 // Math -> 对象
5 // window/obj/console
6 // console.log(typeof Math)
7 // var math = new Math()
8
9 // Math对象的属性
10 // console.log(Math.PI)
11
12 // Math对象的方法
13 // var num = 3.55
14 // console.log(Math.floor(num)) // 3
15 // console.log(Math.ceil(num)) // 4
16 // console.log(Math.round(num)) // 4
17
18 // 另外方法
19 // random: 随机生成 [0, 1)
20 console.log(Math.random())
21 // 需求: [5~50)的随机数
22 // [a, b)
23 // y = a
24 // x = b - a
25 // Math.floor(Math.random() * x) + y
26 for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
27 var randomNum = Math.floor(Math.random() * 45) + 5
28 console.log(randomNum)
29 }
30
31 // Math.pow(x, y)
32 console.log(Math.pow(2, 4))
String类
String也是包装类型
String常见的属性:
- length:获取字符串的长度;
访问字符串的字符
- 使用方法一:通过字符串的索引 str[0]
- 使用方法二:通过str.charAt(pos)方法
- 它们的区别是索引的方式没有找到会返回undefined,而charAt没有找到会返回空字符串;
字符串的遍历
- 方式一:普通for循环
- 方式二:for..of遍历
1 var message = "Hello 你好World"
2 // 1.属性: length
3 console.log(message.length)
4
5 // 2.访问字符串中某个位置的字符
6 console.log(message[4])
7 console.log(message.charAt(4))
8 console.log(message[20])
9 console.log(message.charAt(20))
10
11 // 3.字符串的遍历
12 // for普通遍历
13 for (var i = 0; i < message.length; i++) {
14 console.log(message[i])
15 }
16
17 // for..of的遍历 -> 迭代器
18 // 目前可迭代对象: 字符串/数组
19 // 对象是不支持for..of
20 // String对象内部是将字符串变成了一个可迭代对象
21 for (var char of message) {
22 console.log(char)
23 }
修改字符串
字符串的不可变性
1 var message = "Hello World"
2 // 1.严格的修改字符串, 之前的字符串内部修改掉
3 message[2] = "a"
4
5 console.log(message)
6 // String两个方法:(重要)
7 // toUpperCase: 将所有的字符变成大写
8 // toLowerCase: 将所有的字符变成小写
9 var message1 = message.toUpperCase()
10 console.log(message)
11 console.log("message1:", message1)
12 message = message.toUpperCase()
13
14 var message2 = message.toLowerCase()
15 console.log(message2)
查找字符串
1 var message = "my name is why."
2 var name = "why"
3
4 // 判断一个字符串中是否有另外一个字符串
5 // 1.indexOf(searchString, fromIndex)
6 /*
7 index:
8 情况一: 搜索到, 搜索字符串所在索引位置
9 情况二: 没有搜索到, 返回-1
10 */
11 // var index = message.indexOf(name)
12 // if (message.indexOf(name) !== -1) {
13 // console.log("message中包含name")
14 // } else {
15 // console.log("message不包含name")
16 // }
17
18 // 2.includes: ES6中新增一个方法, 就是用来判断包含关系
19 // if (message.includes(name)) {
20 // console.log("message中包含name")
21 // }
22
23 // 3.startsWith: 是否以xxx开头
24 // if (message.startsWith("my")) {
25 // console.log("message以my开头")
26 // }
27
28 // 4.endsWith: 是否以xxx结束
29 // if (message.endsWith("why")) {
30 // console.log("message以why结尾")
31 // }
32
33 // 5.replace 替换字符串
34 // var newMessage = message.replace("why", "kobe")
35 // console.log(message)
36 // console.log(newMessage)
37 var newName = "kobe"
38 var newMessage = message.replace("why", function() {
39 return newName.toUpperCase()
40 })
41 console.log(newMessage)
截取字符串
1 var message = "Hello World"
2
3 // 获取子字符串
4 // console.log(message.slice(3, 7))
5 // console.log(message.slice(3, -1))
6 // console.log(message.slice(3))
7
8 // substr
9 console.log(message.substr(3, 7))
字符串拼接
1 var str1 = "Hello"
2 var str2 = "World"
3 var str3 = "kobe"
4
5 // 1.字符串拼接
6 // +
7 // var newString = str1 + str2 + str3
8 // console.log(newString)
9 // concat方法: 链式调用
10 var newString2 = str1.concat(str2).concat(str3)
11 var newString3 = str1.concat(str2, str3, "abc", "cba")
12 console.log(newString2)
13 console.log(newString3)
14
15 // 2.删除收尾的空格
16 console.log(" why abc ".trim())
17
18 // 3.字符串切割split
19 var message = "abc-cba-nba-mba"
20 var items = message.split("-")
21 var newMessage = items.join("*")
22 console.log(newMessage)
数组
1
2 // 1.创建数组的方式
3 var names = ["why", "kobe", "james", "curry"]
4
5 var product1 = { name: "苹果", price: 10 }
6 var products = [
7 { name: "鼠标", price: 98 },
8 { name: "键盘", price: 100 },
9 { name: "西瓜", price: 20 },
10 product1
11 ]
12
13 // 2.创建方式二: 类Array
14 var arr1 = new Array()
15 var arr2 = new Array("abc", "cba", "nba") // ["abc", "cba", "nba"]
16 console.log(arr1, arr2)
17
18 // 传入了一个数字, 它默认会当成我们要创建一个对应长度的数组
19 var arr3 = new Array(5) // [empty*5]
20 console.log(arr3, arr3[0])
21 var arr4 = [5]
22
23 // 3.通过索引访问元素
24 console.log(names[0]) // 第一个元素
25 console.log(names[names.length-1]) // 最后一个元素
1 // 对于某一个结构的操作: 增删改查(数据库)
2
3 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba"]
4
5 // 1.访问数组中的元素
6 console.log(names[0])
7 console.log(names.at(0))
8
9 console.log(names[-1])
10 console.log(names.at(-1))
11
12 // 2.修改数组中的元素
13 // names[0] = "why"
14 // console.log(names)
15
16 // 3.新增数组中的元素(了解)
17 // names[3] = "kobe"
18 // 中间empty*6
19 // names[10] = "james"
20 // console.log(names)
21
22 // 4.删除数组中的元素(了解)
23 // delete names[1]
24 // console.log(names)
25 // console.log(names[1])
1 // var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba", "abcd"]
2
3 // 1.在数组的尾部添加和删除元素
4 // // push方法
5 // names.push("why", "kobe")
6 // console.log(names)
7 // // pop方法
8 // names.pop()
9 // names.pop()
10 // console.log(names)
11
12 // // 2.在数组的头部添加和删除元素
13 // // unshift方法
14 // names.unshift("why", "kobe")
15 // console.log(names)
16 // // shift方法
17 // names.shift()
18 // console.log(names)
19
20 // 3. 在任意位置添加/删除/替换元素
21 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba", "abcd"]
22 // 参数一: start, 从什么位置开始操作元素
23 // 参数二: deleteCount, 删除元素的个数
24
25 // 3.1.删除元素
26 // names.splice(1, 2)
27 // console.log(names)
28
29 // 3.2.新增元素
30 // deleteCount: 0, 后面可以添加新的元素
31 // names.splice(1, 0, "why", "kobe")
32 // console.log(names)
33
34 // 3.3.替换元素。.删除2个 加3个
35 names.splice(1, 2, "why", "kobe", "james")
36 console.log(names)
1 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba"]
2
3 // 1.属性length
4 // 获取数组的长度length
5 // console.log(names.length) // 4
6
7 // // length属性可写的(扩容)
8 // names.length = 10
9 // console.log(names)
10
11 // // 设置的length小于原来的元素个数
12 // names.length = 0
13 // console.log(names)
14
15 // 2.数组的遍历
16 // 2.1. 普通的for循环
17 for (var i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
18 console.log(names[i])
19 }
20
21 // 2.2. for..in
22 for (var index in names) {
23 console.log(index, names[index])
24 }
25
26 // 2.3. for..of
27 for (var item of names) {
28 console.log(item)
29 }
1 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba", "why", "kobe"]
2
3 // 1.slice方法: 不会修改原数组
4 // splice有区别: splice修改原有的数组
5 // start 从什么位置开始
6 // end 结束位置, 不包含end本身 ,截取
7 var newNames = names.slice(2, 4)
8 console.log(newNames)
9
10 // 2.concat方法: 将多个数组拼接在一起
11 var names1 = ["abc", "cba"]
12 var names2 = ["nba", "mba"]
13 var names3 = ["why", "kobe"]
14 var newNames2 = names1.concat(names2, names3)
15 console.log(newNames2) // (6)['abc', 'cba', 'nba', 'mba', 'why', 'kobe']
16
17 // 3.join方法: 字符串split
18 console.log(names.join("-")) // abc-cba-nba-mba-why-kobe
数组查找
1 /*
2 indexOf方式.
3 手动for循环
4 数组的find方法
5 */
6
7 // 1.数组中存放的是原始类型
8 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba"]
9
10 // 1.1. indexOf
11 // 可以找到, 返回对应的索引
12 // 没有找到, 返回-1
13 console.log(names.indexOf("nbb"))
14
15
16 // 2.数组中存放的是对象类型
17 // var students = [
18 // { id: 100, name: "why", age: 18 },
19 // { id: 101, name: "kobe", age: 30 },
20 // { id: 102, name: "james", age: 25 },
21 // { id: 103, name: "why", age: 22 }
22 // ]
23
24 // 查找的是id为101的学生信息
25 // 2.1. 自己写一个for循环
26 // var stu = null
27 // for (var i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
28 // if (students[i].id === 101) {
29 // stu = students[i]
30 // break
31 // }
32 // }
33
34 // // 判断上面的算法有没有找到对应的学生
35 // if (stu) {
36 // console.log("找到了对应的101学生", stu)
37 // } else {
38 // console.log("没有找到对应的101学生")
39 // }
40
41 // 2.2. find方法: 高阶函数
42 var students = [
43 { id: 100, name: "why", age: 18 },
44 { id: 101, name: "kobe", age: 30 },
45 { id: 102, name: "james", age: 25 },
46 { id: 103, name: "why", age: 22 }
47 ]
48
49 var stu = students.find(function(item) {
50 if (item.id === 101) return true
51 })
52 console.log(stu)
遍历
1 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba"]
2
3 // forEach函数: 可以帮助我遍历数组
4 // for (var i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
5 // console.log(names[i])
6 // }
7
8 // 1.hyForEach版本一(大部分同学掌握)
9 function hyForEach(fn) {
10 for (var i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
11 fn(names[i], i, names)
12 }
13 }
14
15 hyForEach(function(item, index, names) {
16 console.log("-------", item, index, names)
17 })
18
19 // 2.hyForEach版本二
20 // function hyForEach(fn, arr) {
21 // for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
22 // fn(arr[i], i, arr)
23 // }
24 // }
25
26 // hyForEach(function(item, index, names) {
27 // console.log("-------", item, index, names)
28 // }, names)
29
30 // hyForEach(function(item, index, names) {
31 // console.log("-------", item, index, names)
32 // }, [123, 321, 111, 222])
33
34
35 // 3.hyForEach版本三
36 names.hyForEach = function(fn) {
37 for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
38 fn(this[i], i, this)
39 }
40 }
41
42 names.hyForEach(function(item, index, names) {
43 console.log("-------", item, index, names)
44 })
45
46 names.forEach(function(item, index, names) {
47 console.log("-------", item, index, names)
48 })
49
50
51 // 4.hyForEach版本四(了解)
52 // Array.prototype.hyForEach = function(fn, thisArgs) {
53 // for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
54 // fn(this[i], i, this)
55 // }
56 // }
57 //
58 // names.hyForEach(function(item, index, names) {
59 // console.log("------", item, index, names)
60 // })
61 //
62 // var students = [
63 // { id: 100, name: "why", age: 18 },
64 // { id: 101, name: "kobe", age: 30 },
65 // { id: 102, name: "james", age: 25 },
66 // { id: 103, name: "why", age: 22 }
67 // ]
68 //
69 // students.hyForEach(function(item, index, stus) {
70 // console.log("++++++", item, index, stus)
71 // })
排序
1
2 // var nums = [20, 4, 10, 15, 100, 88]
3
4 // // sort: 排序
5 // nums.sort(function(item1, item2) {
6 // // item1和item2进行比较
7 // // 返回是 整数
8 // // 谁小谁在前
9 // // return item1 - item2
10 // return item2 - item1
11 // })
12
13 // console.log(nums)
14 // console.log(nums.reverse())
15
16
17 // 复杂类型的排序
18 var students = [
19 { id: 100, name: "why", age: 18 },
20 { id: 101, name: "kobe", age: 30 },
21 { id: 102, name: "james", age: 25 },
22 { id: 103, name: "curry", age: 22 }
23 ]
24
25 students.sort(function(item1, item2) {
26 return item1.age - item2.age
27 })
28 console.log(students)
高阶函数
1
2 // 1.forEach函数
3 var names = ["abc", "cba", "nba", "mba"]
4
5 // 三种方式, 新增一种方式
6 names.forEach(function(item) {
7 console.log(item, this)
8 }, { name: "why" })
9
10 // 2.filter函数: 过滤
11 // var nums = [11, 20, 55, 100, 88, 32]
12 // 2.1. for循环实现
13 // var newNums = []
14 // for (var item of nums) {
15 // if (item % 2 === 0) {
16 // newNums.push(item)
17 // }
18 // }
19 // 2.2. filter实现
20 // var newNums = nums.filter(function(item) {
21 // return item % 2 === 0
22 // })
23 // console.log(newNums)
24
25
26 // 3.map函数: 映射
27 // var nums = [11, 20, 55, 100, 88, 32]
28 // var newNums = nums.map(function(item) {
29 // return item * item
30 // })
31 // console.log(newNums)
32
33 // 4.reduce
34 // var nums = [11, 20, 55, 100, 88, 32]
35 // var result = 0
36 // for (var item of nums) {
37 // result += item
38 // }
39 // console.log(result)
40 // 第一次执行: preValue->0 item->11
41 // 第二次执行: preValue->11 item->20
42 // 第三次执行: preValue->31 item->55
43 // 第四次执行: preValue->86 item->100
44 // 第五次执行: preValue->186 item->88
45 // 第六次执行: preValue->274 item->32
46 // 最后一次执行的时候 preValue + item, 它会作为reduce的返回值
47
48 // initialValue: 初始化值, 第一次执行的时候, 对应的preValue
49 // 如果initialValue没有传呢?
50 // var result = nums.reduce(function(preValue, item) {
51 // console.log(`preValue:${preValue} item:${item}`)
52 // return preValue + item
53 // }, 0)
54 // console.log(result)
55
56 // reduce练习
57 // var products = [
58 // { name: "鼠标", price: 88, count: 3 },
59 // { name: "键盘", price: 200, count: 2 },
60 // { name: "耳机", price: 9.9, count: 10 },
61 // ]
62 // var totalPrice = products.reduce(function(preValue, item) {
63 // return preValue + item.price * item.count
64 // }, 0)
65 // console.log(totalPrice)
66
67
68 // 综合练习:
69 var nums = [11, 20, 55, 100, 88, 32]
70
71 // 过滤所有的偶数, 映射所有偶数的平方, 并且计算他们的和
72 // var total = nums.filter(function(item) {
73 // return item % 2 === 0
74 // }).map(function(item) {
75 // return item * item
76 // }).reduce(function(preValue, item) {
77 // return preValue + item
78 // }, 0)
79 // console.log(total)
80
81 // var total = nums.filter(item => item % 2 === 0)
82 // .map(item => item * item)
83 // .reduce((preValue, item) => preValue + item, 0)
84 // console.log(total)
DOM
DOM相当于是JavaScript和HTML、CSS之间的桥梁
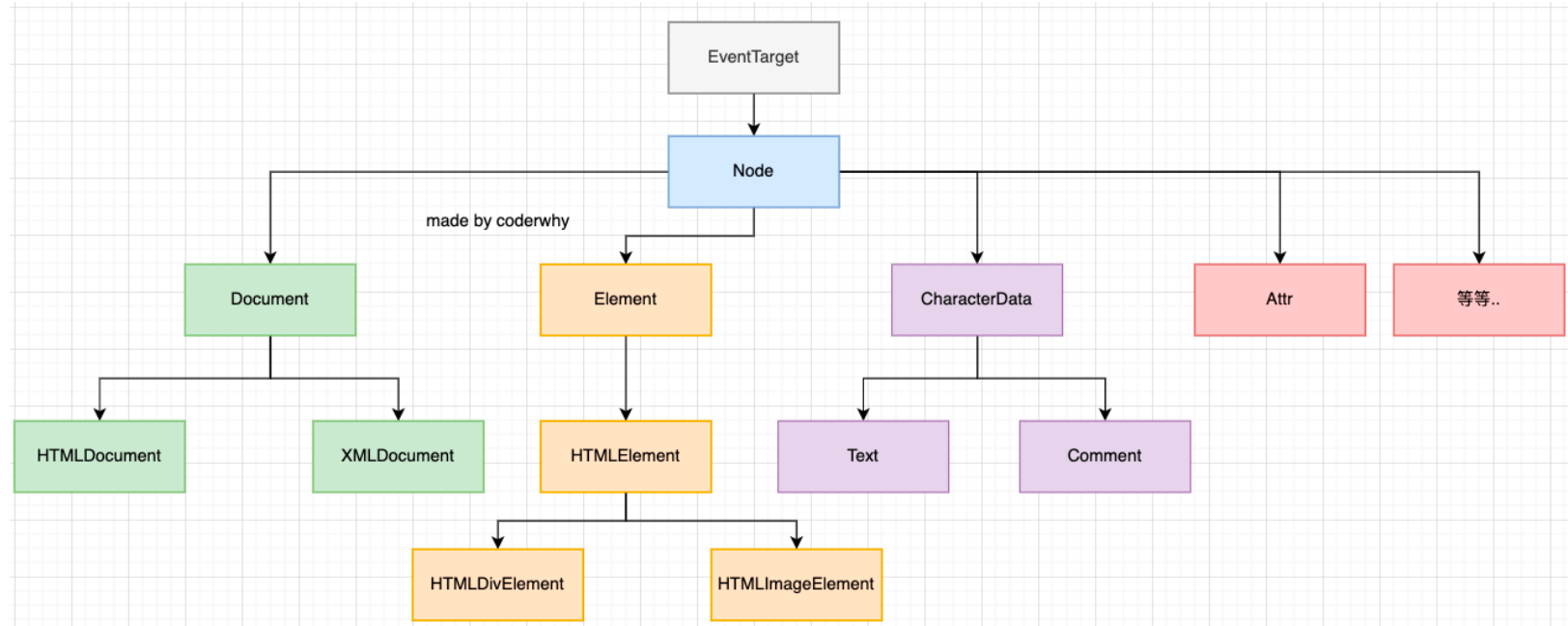
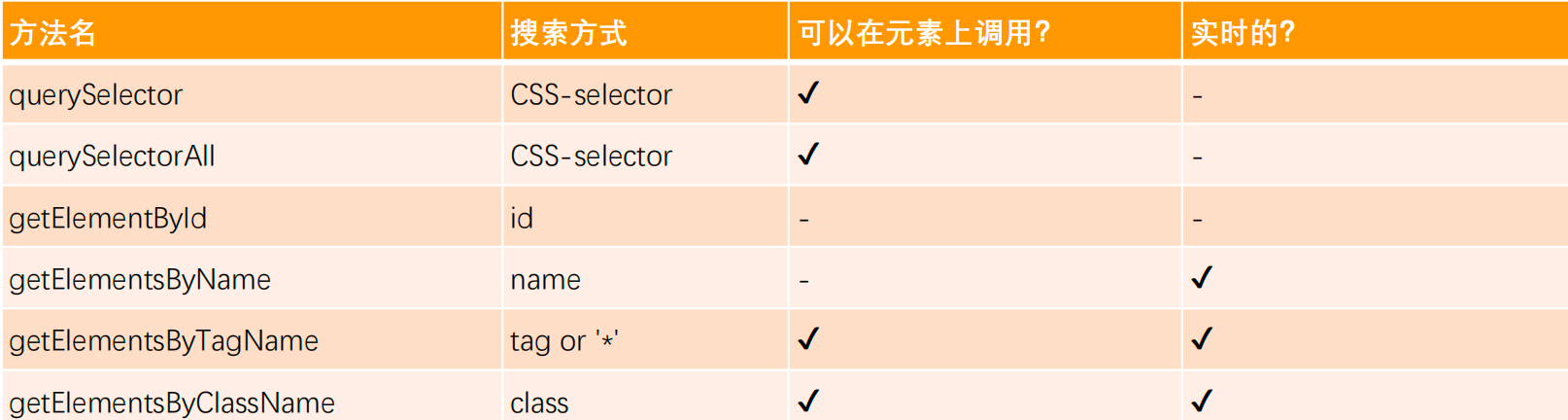
获取元素的方法
nodeType
dataset
1 <div id="abc" class="box"
2 data-age="18" data-height="1.88"></div>
3
4 <script>
5 var boxEl = document.querySelector(".box")
6 // 小程序开发中使用
7 console.log(boxEl.dataset.age)
8 console.log(boxEl.dataset.height)
9 </script>
json
1 var obj = {
2 name: "why",
3 age: 18,
4 friend: {
5 name: "kobe"
6 }
7 }
8
9 console.log(obj.name, obj.age)
10
11 // 1.将obj对象进行序列化
12 var objJSONString = JSON.stringify(obj)
13 console.log(objJSONString)
14
15 // 2.将对象存储到localStorage
16 localStorage.setItem("info", objJSONString)
17
18 var item = localStorage.getItem("info")
19 console.log(item, typeof item)
20
21 // 3.将字符串转回到对象(反序列化)
22 var newObj = JSON.parse(item)
23 console.log(newObj)
24
25
26 // reviver 参数
27 var newObj2 = JSON.parse(item, function(key, value) {
28 if (key === "age") {
29 return value + 2
30 }
31 return value
32 })
33 console.log(newObj2) // age属性=20
1 var obj = {
2 name: "why",
3 age: 18,
4 friend: {
5 name: "kobe"
6 },
7 // toJSON: function() {
8 // return "123"
9 // }
10 }
11
12 // 1.replacer参数
13 var objJSONString = JSON.stringify(obj, function(key, value) {
14 if (key === "name") {
15 return "coderwhy"
16 }
17 return value
18 }, "")
19 console.log(objJSONString)
20
21 // 2.space参数
22 // var objJSONString = JSON.stringify(obj, null, 4)
23 // console.log(objJSONString)
24
25 // // 3.如果对象本身有显示toJSON方法, 那么直接调用toJSON方法
26 // var objJSONString = JSON.stringify(obj)
27 // console.log(objJSONString)
BOM:浏览器对象模型
- window:包括全局属性、方法,控制浏览器窗口相关的属性、方法;
- location:浏览器连接到的对象的位置(URL);
- history:操作浏览器的历史;
- navigator:用户代理(浏览器)的状态和标识(很少用到);
- screen:屏幕窗口信息(很少用到
window对象
window对象在浏览器中可以从两个视角来看待
视角一:全局对象。
我们知道ECMAScript其实是有一个全局对象的,这个全局对象在Node中是global;
在浏览器中就是window对象;
视角二:浏览器窗口对象。
作为浏览器窗口时,提供了对浏览器操作的相关的API;
事实上对于浏览器和Node中全局对象名称不一样的情况,目前已经指定了对应的标准,称之为globalThis,并且大多数现代浏览器都支持它;
- 放在window对象上的所有属性都可以被访问;
- 使用var定义的变量会被添加到window对象中;(仅针对浏览器,node 不是这样的)
- window默认给我们提供了全局的函数和类:setTimeout、Math、Date、Object等;
大量的属性、方法、事件 查看文档 : https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Window
location对象
1// 1.完整的URL
2 console.log(location.href)
3 // 2.获取URL信息
4 console.log(location.hostname)
5 console.log(location.host)
6 console.log(location.protocol)
7 console.log(location.port)
8 console.log(location.pathname)
9 console.log(location.search)
10 console.log(location.hash)
11
12
13 // 3.location方法
14 var btns = document.querySelectorAll("button")
15 btns[0].onclick = function() {
16 location.assign("http://www.baidu.com")
17 }
18 btns[1].onclick = function() {
19 location.replace("http://www.baidu.com")
20 }
21 btns[2].onclick = function() {
22 location.reload()
23 }
24
25
26 // 4.URLSearchParams
27 var urlSearchString = "?name=why&age=18&height=1.88"
28 var searchParams = new URLSearchParams(urlSearchString)
29 console.log(searchParams.get("name"))
30 console.log(searchParams.get("age"))
31 console.log(searchParams.get("height"))
32
33 searchParams.append("address", "广州市")
34 console.log(searchParams.get("address"))
35 console.log(searchParams.toString())
history 对象
有两个属性:
- length:会话中的记录条数;
- state:当前保留的状态值;
有五个方法:
- back():返回上一页,等价于history.go(-1);
- forward():前进下一页,等价于history.go(1);
- go():加载历史中的某一页;
- pushState():打开一个指定的地址;
- replaceState():打开一个新的地址,并且使用replace;
history和hash目前是vue、react等框架实现路由的底层原理
screen
screen主要记录的是浏览器窗口外面的客户端显示器的信息:

1 // 前端路由核心: 修改了URL, 但是页面不刷新
2 // 1> 修改hash值
3 // 2> 修改history
4
5 // 1.history对应的属性
6 console.log(history.length)
7 console.log(history.state)
8
9 // 2.修改history
10 var btnEl = document.querySelector("button")
11 btnEl.onclick = function() {
12 // history.pushState({ name: "why", age: 18 }, "", "/why")
13 history.replaceState({ name: "why", age: 18 }, "", "/why")
14 }
15
16 var backBtnEl = document.querySelector(".back")
17 backBtnEl.onclick = function() {
18 // history.back()
19 // history.forward()
20 // 类似于上面的两个方法, 只是可以传入层级
21 // history.go(-2)
22 }
navigator对象

1 console.log(navigator.userAgent)
2 console.log(navigator.vendor)
3 console.log(navigator.platform)
4 console.log(navigator.oscpu)