学习腾讯大佬讲解go语言项目开发实战, 有些关于go项目开发的,非专栏内容也会写在这篇文章里
课程地址:https://time.geekbang.org/column/intro/100079601
01IAM系统概述
这篇主要将 一个iam系统的架构 ,先了解项目架构,不然后面学技术都不知道为啥干啥还是不太好,虽然这篇文章没啥技术点可言,学习下他干项目的思路吧,为啥这么架构。
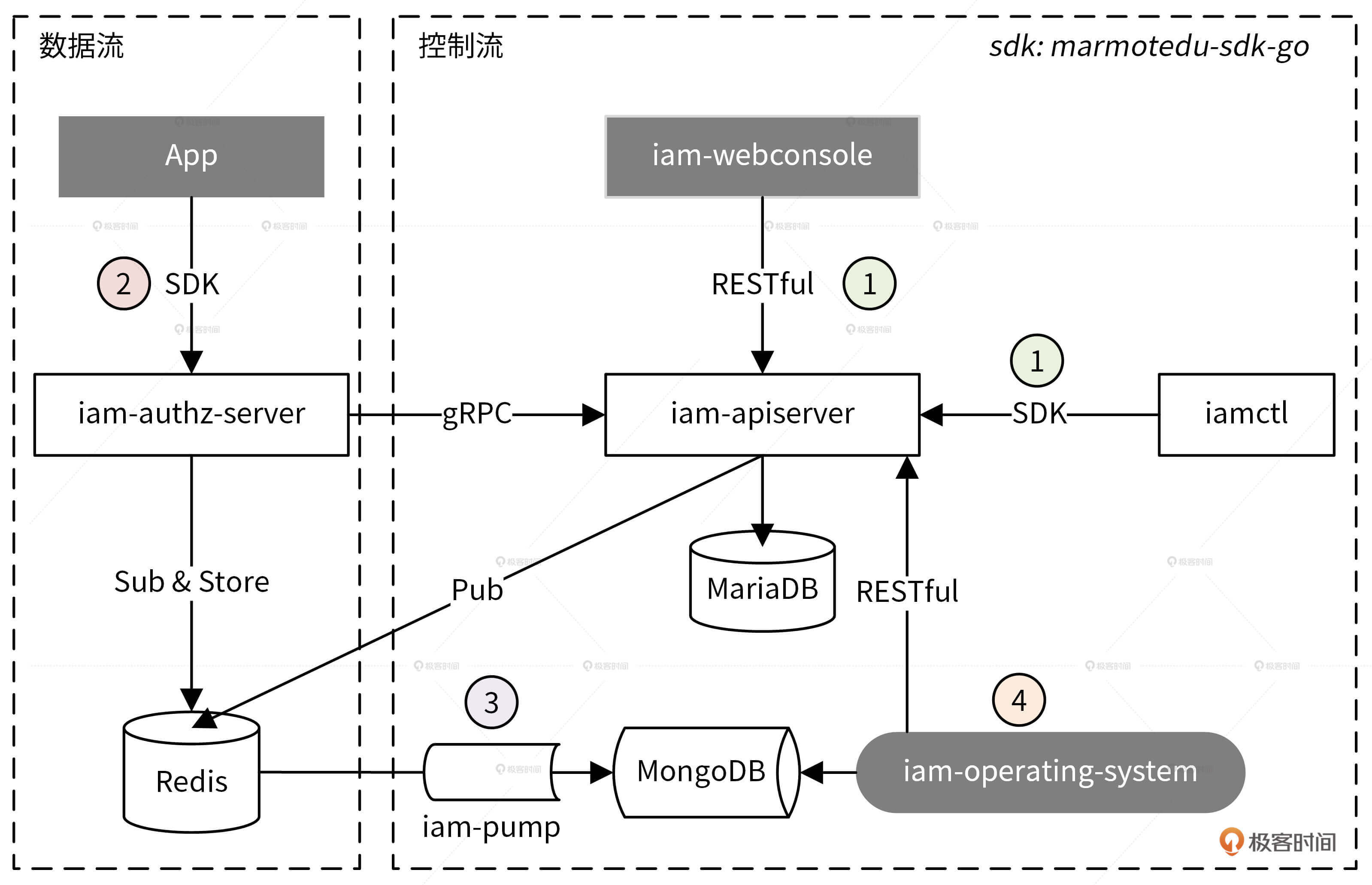
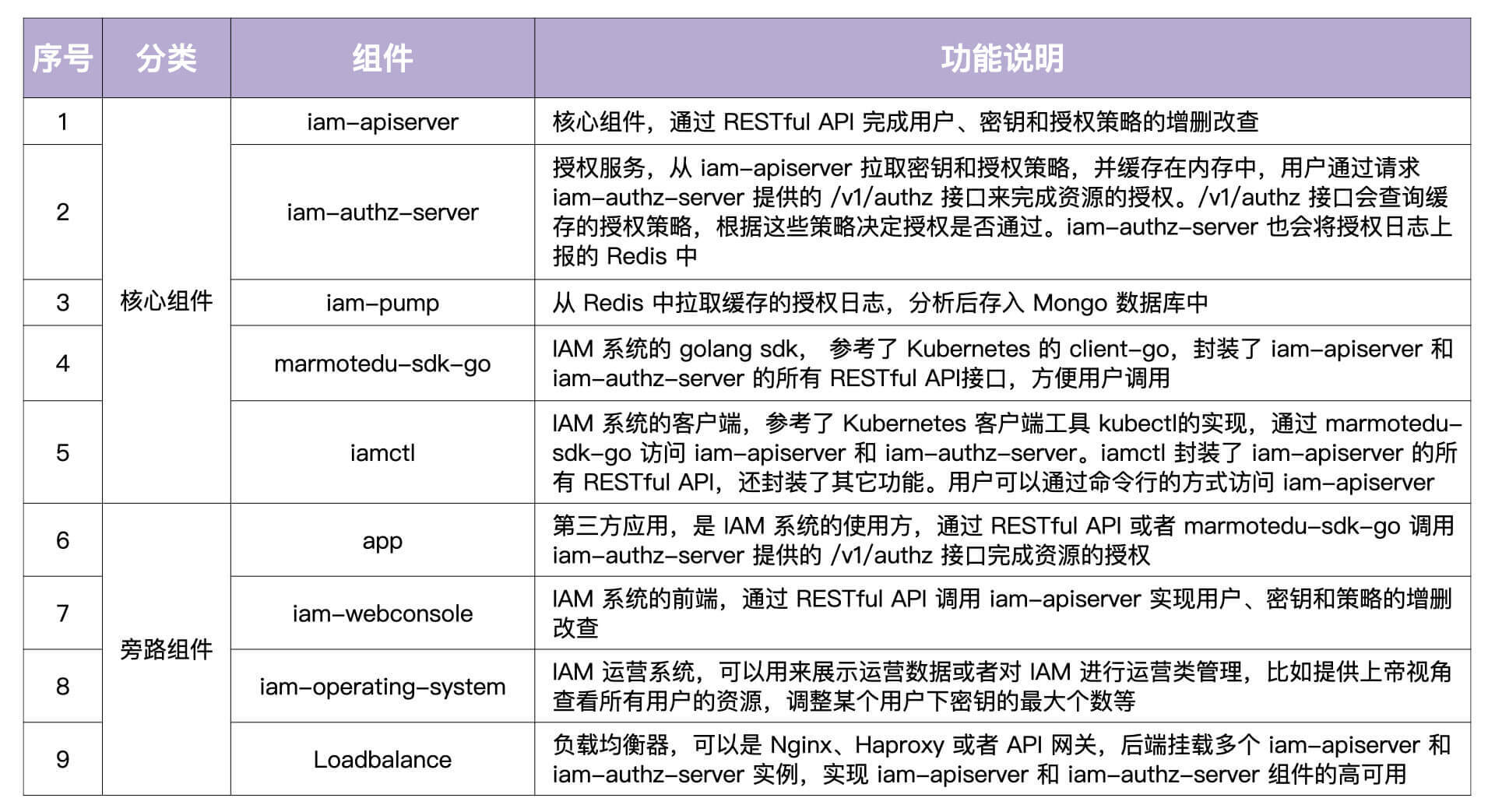
- 用户通过 iam-webconsole(RESTful API)或 iamctl(sdk marmotedu-sdk-go)客户端请求 iam-apiserver 提供的 RESTful API 接口完成用户、密钥、授权策略的增删改查,iam-apiserver 会将这些资源数据持久化存储在 MySQL 数据库中. 通信安全考虑,这里都用https方式来访问
- 用户可以通过请求 iam-authz-server 提供的 /v1/authz 接口进行资源授权。 iam-authz-server 通过调用 iam-apiserver 提供的 gRPC 接口,将密钥和授权策略信息缓存到内存中。 采用redis 的发布订阅模式,保证 缓存信息 和 iam-apiserver中的数据一致
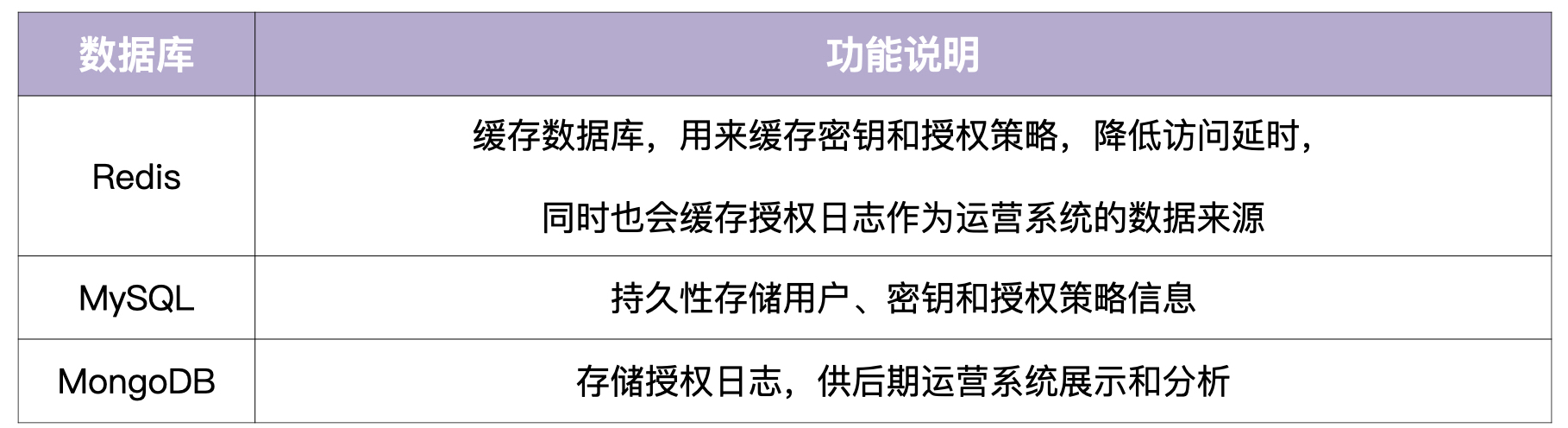
- 授权日志数据分析。 iam-authz-server 会将授权日志上报到 Redis 高速缓存中。 一个组件会去消费获得到数据,并清理数据,存到mongodb中,,供运营系统 iam-operating-system 查询
- 运营平台授权数据展示。 iam-operating-system 是 IAM 的运营系统,它可以通过查询 MongoDB 获取并展示运营数据
然后讲了 前后端分离架构 和 mvc 架构的特点,和使用场景。 这个自己看着办吧。 只有合适的架构。 需要根据公司情况而定。
02环境安装
作为多年的程序员,环境还是没啥大问题,有几个自己不太懂的技能点做个笔记即可。
使用普通用户来操作linux ,将普通用户添加到 sudoer 中即可
1sed -i '/^root.*ALL=(ALL).*ALL/a\going\tALL=(ALL) \tALL' /etc/sudoers
这个就是在root xxx 后面追加一行,可以完全vim 这个文件 加上,我是ubuntu系统加上下面即可 可能和文章的centos8.2有点不一样而已。
1going ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
protoc,protoc-gen-go 安装 以前早就装过,之前公司开发的社交项目就是用grpc做服务的。
至于开发工具选择,选择自己喜欢的就行,他用spacevim ,我还是选择我的goland 。 毕竟要钱的一般都比不要的好 。😄
03项目部署
根据安装稳定,选择ubuntu系列,稍微改改安装即可,作为多年老程序员没啥问题。
顺利安装成功。 我把所有密码改成了123456 ,方便自己输入。 这个项目还是打算好好研究源码的要。
程序目录说明
一些我的目录说明,以防忘记了
- 项目目录 /home/www/workspace/golang/src/github.com/marmotedu/iam
- /home/vagrant/bin/iamctl 命令行
- /etc/iam/iam-apiserver.yaml
- /etc/iam/iam-authz-server.yaml
- /etc/iam/iam-pump.yaml
1vagrant@ubuntu2204:/etc/iam/cert$ ls
2ca-config.json ca-key.pem iam-apiserver.pem
3ca.csr ca.pem iam-authz-server-key.pem
4ca-csr.json iam-apiserver-key.pem iam-authz-server.pem
5
6vagrant@ubuntu2204:/opt/iam/bin$ ls
7iam-apiserver iam-authz-server iam-pump
1vagrant@ubuntu2204:/home/www/workspace/golang/src/github.com/marmotedu/iam$ ps -ef | grep iam
2root 26827 1 0 15:21 ? 00:00:02 /opt/iam/bin/iam-apiserver --config=/etc/iam/iam-apiserver.yaml
3root 28020 1 0 15:45 ? 00:00:03 /opt/iam/bin/iam-authz-server --config=/etc/iam/iam-authz-server.yaml
4root 28955 1 1 16:00 ? 00:00:00 /opt/iam/bin/iam-pump --config=/etc/iam/iam-pump.yaml
5
6vagrant@ubuntu2204:/etc/systemd/system$ ls -al | grep iam
7-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 419 Apr 25 15:20 iam-apiserver.service
8-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 433 Apr 25 15:45 iam-authz-server.service
9-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 401 Apr 25 16:00 iam-pump.service
system service 编写
/etc/systemd/system/iam-apiserver.service
1[Unit]
2Description=IAM APIServer
3Documentation=https://github.com/marmotedu/iam/blob/master/init/README.md
4
5[Service]
6WorkingDirectory=/data/iam/iam-apiserver
7ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/mkdir -p /data/iam/iam-apiserver
8ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/mkdir -p /var/log/iam
9ExecStart=/opt/iam/bin/iam-apiserver --config=/etc/iam/iam-apiserver.yaml
10Restart=always
11RestartSec=5
12StartLimitInterval=0
13
14[Install]
15WantedBy=multi-user.target
1sudo systemctl daemon-reload
2sudo systemctl enable iam-apiserver
3sudo systemctl restart iam-apiserver
4man iam-apiserver
5iamctl version -o yaml
04项目规范设计(上)
代码规定、目录规范、接口规范、错误码规范
- 非编码类规范,主要包括开源规范、文档规范、版本规范、Commit 规范和发布规范。
- 编码类规范,则主要包括目录规范、代码规范、接口规范、日志规范和错误码规范。
开源协议
开源规范,开源协议大致了解下
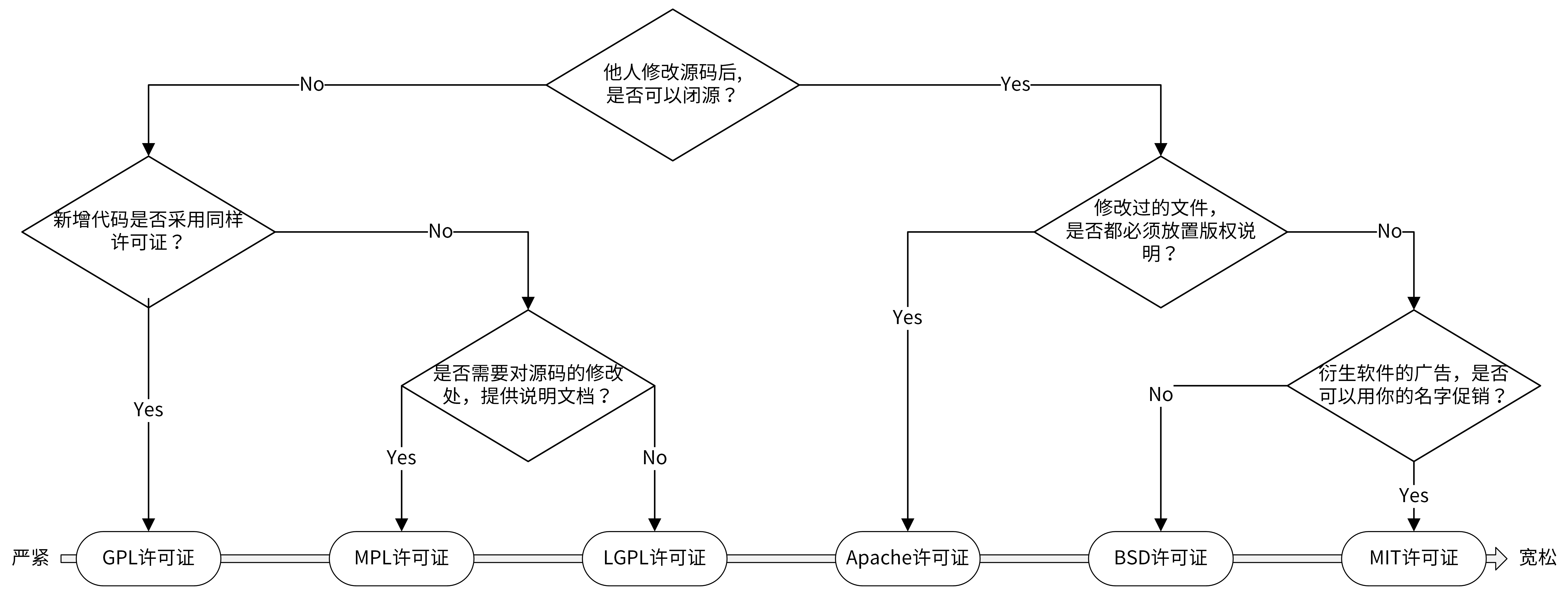
大型公司的开源项目通常会采用 Apache 2.0 开源协议,使用者也可以在需要的时候修改代码来满足需要
一般自己的项目采用mtg协议即可
文档规范
readme模板
1# 项目名称
2
3<!-- 写一段简短的话描述项目 -->
4
5## 功能特性
6
7<!-- 描述该项目的核心功能点 -->
8
9## 软件架构(可选)
10
11<!-- 可以描述下项目的架构 -->
12
13## 快速开始
14
15### 依赖检查
16
17<!-- 描述该项目的依赖,比如依赖的包、工具或者其他任何依赖项 -->
18
19### 构建
20
21<!-- 描述如何构建该项目 -->
22
23### 运行
24
25<!-- 描述如何运行该项目 -->
26
27## 使用指南
28
29<!-- 描述如何使用该项目 -->
30
31## 如何贡献
32
33<!-- 告诉其他开发者如果给该项目贡献源码 -->
34
35## 社区(可选)
36
37<!-- 如果有需要可以介绍一些社区相关的内容 -->
38
39## 关于作者
40
41<!-- 这里写上项目作者 -->
42
43## 谁在用(可选)
44
45<!-- 可以列出使用本项目的其他有影响力的项目,算是给项目打个广告吧 -->
46
47## 许可证
48
49<!-- 这里链接上该项目的开源许可证 -->
1docs
2├── devel # 开发文档,可以提前规划好,英文版文档和中文版文档
3│ ├── en-US/ # 英文版文档,可以根据需要组织文件结构
4│ └── zh-CN # 中文版文档,可以根据需要组织文件结构
5│ └── development.md # 开发手册,可以说明如何编译、构建、运行项目
6├── guide # 用户文档
7│ ├── en-US/ # 英文版文档,可以根据需要组织文件结构
8│ └── zh-CN # 中文版文档,可以根据需要组织文件结构
9│ ├── api/ # API文档
10│ ├── best-practice # 最佳实践,存放一些比较重要的实践文章
11│ │ └── authorization.md
12│ ├── faq # 常见问题
13│ │ ├── iam-apiserver
14│ │ └── installation
15│ ├── installation # 安装文档
16│ │ └── installation.md
17│ ├── introduction/ # 产品介绍文档
18│ ├── operation-guide # 操作指南,里面可以根据RESTful资源再划分为更细的子目录,用来存放系统核心/全部功能的操作手册
19│ │ ├── policy.md
20│ │ ├── secret.md
21│ │ └── user.md
22│ ├── quickstart # 快速入门
23│ │ └── quickstart.md
24│ ├── README.md # 用户文档入口文件
25│ └── sdk # SDK文档
26│ └── golang.md
27└── images # 图片存放目录
28 └── 部署架构v1.png
接口文档
接口文档有四种编写方式,包括编写 Word 格式文档、借助工具编写、通过注释生成和编写(swagger)、 Markdown 格式文档。
版本规范
项目中的组件也建议加上版本。
主版本号.次版本号.修订号(X.Y.Z)
建议 0.1.0 作为第一个开发版本号
05项目规范下(下) commit规范
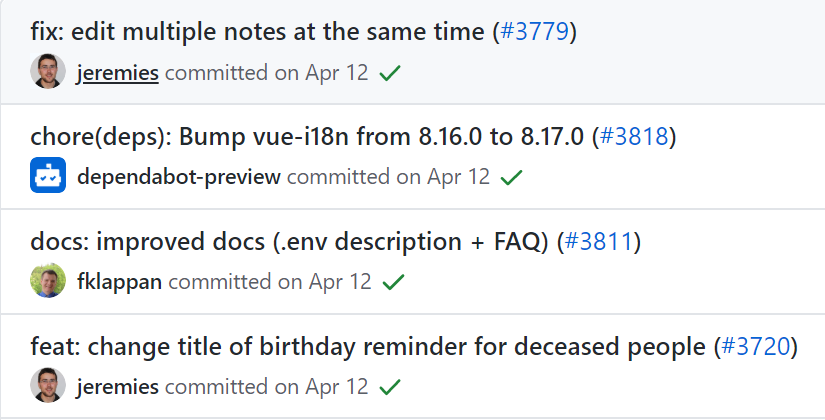
在 Angular 规范中,Commit Message 包含三个部分,分别是 Header、Body 和 Footer,格式如下:
1<type>[optional scope]: <description>
2// 空行
3[optional body]
4// 空行
5[optional footer(s)]
如
1fix(core): remove xxxx
2
3this api is xxxx
4
5PR close #xxx
commit type 类型
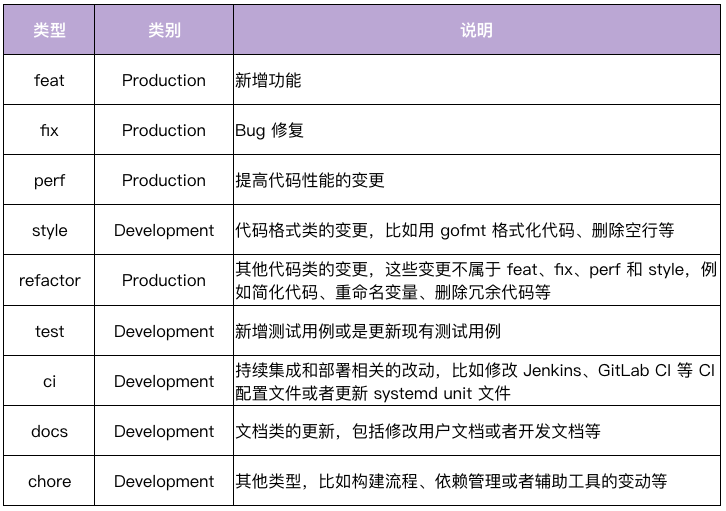
Header中 第二个字段 scope 表示影响范围
Body 它是对本次 commit 的更详细描述,是可选的
Footer 主要用来说明本次 commit 导致的后果
commit 时机
比如修复完一个 bug、开发完一个小功能,或者开发完一个完整的功能,测试通过后就提交
合并提交
git rebase -i commit-id
修改 Commit Message
2种方式
-
git commit –amend:修改最近一次 commit 的 message;
-
git rebase -i:修改某次 commit 的 message。
Commit Message 规范自动化
这个没用过。 先放放,目前没有使用场景。
06目录结构设计
https://github.com/golang-standards/project-layout
1├── api
2│ ├── openapi
3│ └── swagger
4├── build
5│ ├── ci
6│ ├── docker
7│ │ ├── iam-apiserver
8│ │ ├── iam-authz-server
9│ │ └── iam-pump
10│ ├── package
11├── CHANGELOG
12├── cmd
13│ ├── iam-apiserver
14│ │ └── apiserver.go
15│ ├── iam-authz-server
16│ │ └── authzserver.go
17│ ├── iamctl
18│ │ └── iamctl.go
19│ └── iam-pump
20│ └── pump.go
21├── configs
22├── CONTRIBUTING.md
23├── deployments
24├── docs
25│ ├── devel
26│ │ ├── en-US
27│ │ └── zh-CN
28│ ├── guide
29│ │ ├── en-US
30│ │ └── zh-CN
31│ ├── images
32│ └── README.md
33├── examples
34├── githooks
35├── go.mod
36├── go.sum
37├── init
38├── internal
39│ ├── apiserver
40│ │ ├── api
41│ │ │ └── v1
42│ │ │ └── user
43│ │ ├── apiserver.go
44│ │ ├── options
45│ │ ├── service
46│ │ ├── store
47│ │ │ ├── mysql
48│ │ │ ├── fake
49│ │ └── testing
50│ ├── authzserver
51│ │ ├── api
52│ │ │ └── v1
53│ │ │ └── authorize
54│ │ ├── options
55│ │ ├── store
56│ │ └── testing
57│ ├── iamctl
58│ │ ├── cmd
59│ │ │ ├── completion
60│ │ │ ├── user
61│ │ └── util
62│ ├── pkg
63│ │ ├── code
64│ │ ├── options
65│ │ ├── server
66│ │ ├── util
67│ │ └── validation
68├── LICENSE
69├── Makefile
70├── _output
71│ ├── platforms
72│ │ └── linux
73│ │ └── amd64
74├── pkg
75│ ├── util
76│ │ └── genutil
77├── README.md
78├── scripts
79│ ├── lib
80│ ├── make-rules
81├── test
82│ ├── testdata
83├── third_party
84│ └── forked
85└── tools
07-工作流设计:如何设计合理的多人开发模式?
git flow 工作流 , 各分支都有自己的用途,如开发分支,预发布分支,线上分支等。
功能分支工作流 : 只有master 分支和 开发分支, 开发分支最终都合并到master 上。
10 怎么写出优雅的Go项目?
好的文档 readme模版: https://readme.so/editor
makefile, 代码生成
对接CI/CD
代码规范
Effective Go :高效Go编程,由Golang官方编写,里面包含了编写Go代码的一些建议,也可以理解为最佳实践。
Go Code Review Comments :Golang官方编写的Go最佳实践,作为Effective Go的补充。
Style guideline for Go packages :包含了如何组织Go包、如何命名Go包、如何写Go包文档的一些建议。
Go语言的静态代码检查工具有很多,目前用的最多的是 golangci-lint
编写可测试的代码
代码可测试,可mock ,通过依赖注入的方式去编写代码。
常用的Mock工具,有这么几个:
golang/mock ,是官方提供的Mock框架。它实现了基于interface的Mock功能,能够与Golang内置的testing包做很好的集成,是最常用的Mock工具。golang/mock提供了mockgen工具用来生成interface对应的Mock源文件。
sqlmock ,可以用来模拟数据库连接。数据库是项目中比较常见的依赖,在遇到数据库依赖时都可以用它。
httpmock ,可以用来Mock HTTP请求。
bouk/monkey ,猴子补丁,能够通过替换函数指针的方式来修改任意函数的实现。如果golang/mock、sqlmock和httpmock这几种方法都不能满足我们的需求,我们可以尝试通过猴子补丁的方式来Mock依赖。可以这么说,猴子补丁提供了单元测试 Mock 依赖的最终解决方案。
单元测试覆盖率 :
1$ go test -race -cover -coverprofile=./coverage.out -timeout=10m -short -v ./...
2$ go tool cover -func ./coverage.out
自动生成代码
- 错误码、错误码说明文档。
- 自动生成缺失的doc.go文件。
- 利用gotests工具,自动生成单元测试用例。
- 使用Swagger工具,自动生成Swagger文档。
- 使用Mock工具,自动生成接口的Mock实例。
11 Go常用设计模式
单例
1package singleton
2
3import (
4 "sync"
5)
6
7type singleton struct {
8}
9
10var ins *singleton
11var once sync.Once
12
13func GetInsOr() *singleton {
14 once.Do(func() {
15 ins = &singleton{}
16 })
17 return ins
18}
在实际开发中,我建议返回非指针的实例,因为我们主要是想通过创建实例,调用其提供的方法,而不是对实例做更改。如果需要对实例做更改,可以实现SetXXX的方法。通过返回非指针的实例,可以确保实例的属性,避免属性被意外/任意修改。
简单工厂、抽象工厂
简单工厂
1type Person struct {
2 Name string
3 Age int
4}
5
6func (p Person) Greet() {
7 fmt.Printf("Hi! My name is %s", p.Name)
8}
9
10func NewPerson(name string, age int) *Person {
11 return Person{
12 Name: name,
13 Age: age
14 }
15}
抽象工厂
返回的是接口
1type Person interface {
2 Greet()
3}
4
5type person struct {
6 name string
7 age int
8}
9
10func (p person) Greet() {
11 fmt.Printf("Hi! My name is %s", p.name)
12}
13
14// Here, NewPerson returns an interface, and not the person struct itself
15func NewPerson(name string, age int) Person {
16 return person{
17 name: name,
18 age: age
19 }
20}
策略模式
1package strategy
2
3// 策略模式
4
5// 定义一个策略类
6type IStrategy interface {
7 do(int, int) int
8}
9
10// 策略实现:加
11type add struct{}
12
13func (*add) do(a, b int) int {
14 return a + b
15}
16
17// 策略实现:减
18type reduce struct{}
19
20func (*reduce) do(a, b int) int {
21 return a - b
22}
23
24// 具体策略的执行者
25type Operator struct {
26 strategy IStrategy
27}
28
29// 设置策略
30func (operator *Operator) setStrategy(strategy IStrategy) {
31 operator.strategy = strategy
32}
33
34// 调用策略中的方法
35func (operator *Operator) calculate(a, b int) int {
36 return operator.strategy.do(a, b)
37}
测试:
1func TestStrategy(t *testing.T) {
2 operator := Operator{}
3
4 operator.setStrategy(&add{})
5 result := operator.calculate(1, 2)
6 fmt.Println("add:", result)
7
8 operator.setStrategy(&reduce{})
9 result = operator.calculate(2, 1)
10 fmt.Println("reduce:", result)
11}
模版模式
1package template
2
3import "fmt"
4
5type Cooker interface {
6 fire()
7 cooke()
8 outfire()
9}
10
11// 类似于一个抽象类
12type CookMenu struct {
13}
14
15func (CookMenu) fire() {
16 fmt.Println("开火")
17}
18
19// 做菜,交给具体的子类实现
20func (CookMenu) cooke() {
21}
22
23func (CookMenu) outfire() {
24 fmt.Println("关火")
25}
26
27// 封装具体步骤
28func doCook(cook Cooker) {
29 cook.fire()
30 cook.cooke()
31 cook.outfire()
32}
33
34type XiHongShi struct {
35 CookMenu
36}
37
38func (*XiHongShi) cooke() {
39 fmt.Println("做西红柿")
40}
41
42type ChaoJiDan struct {
43 CookMenu
44}
45
46func (ChaoJiDan) cooke() {
47 fmt.Println("做炒鸡蛋")
48}
测试:
1func TestTemplate(t *testing.T) {
2 // 做西红柿
3 xihongshi := &XiHongShi{}
4 doCook(xihongshi)
5
6 fmt.Println("\n=====> 做另外一道菜")
7 // 做炒鸡蛋
8 chaojidan := &ChaoJiDan{}
9 doCook(chaojidan)
10
11}
选项模式
1package options
2
3import (
4 "time"
5)
6
7type Connection struct {
8 addr string
9 cache bool
10 timeout time.Duration
11}
12
13const (
14 defaultTimeout = 10
15 defaultCaching = false
16)
17
18type options struct {
19 timeout time.Duration
20 caching bool
21}
22
23// Option overrides behavior of Connect.
24type Option interface {
25 apply(*options)
26}
27
28type optionFunc func(*options)
29
30func (f optionFunc) apply(o *options) {
31 f(o)
32}
33
34func WithTimeout(t time.Duration) Option {
35 return optionFunc(func(o *options) {
36 o.timeout = t
37 })
38}
39
40func WithCaching(cache bool) Option {
41 return optionFunc(func(o *options) {
42 o.caching = cache
43 })
44}
45
46// Connect creates a connection.
47func Connect(addr string, opts ...Option) (*Connection, error) {
48 options := options{
49 timeout: defaultTimeout,
50 caching: defaultCaching,
51 }
52
53 for _, o := range opts {
54 o.apply(&options)
55 }
56
57 return &Connection{
58 addr: addr,
59 cache: options.caching,
60 timeout: options.timeout,
61 }, nil
62}
12-API风格(上):如何设计RESTfulAPI
api 版本
API版本有不同的标识方法,在RESTful API开发中,通常将版本标识放在如下3个位置:
- URL中,比如/v1/users。
- HTTP Header中,比如Accept: vnd.example-com.foo+json; version=1.0。
- Form参数中,比如/users?version=v1。
API命名
API通常的命名方式有三种,分别是驼峰命名法(serverAddress)、蛇形命名法(server_address)和脊柱命名法(server-address)。
驼峰命名法和蛇形命名法都需要切换输入法,会增加操作的复杂性,也容易出错,所以这里建议用脊柱命名法。GitHub API用的就是脊柱命名法,例如 selected-actions
api 域名
API的域名设置主要有两种方式:
https://marmotedu.com/api ,这种方式适合API将来不会有进一步扩展的情况,比如刚开始marmotedu.com域名下只有一套API系统,未来也只有这一套API系统。
https://iam.api.marmotedu.com,如果marmotedu.com域名下未来会新增另一个系统API,这时候最好的方式是每个系统的API拥有专有的API域名,比如:storage.api.marmotedu.com,network.api.marmotedu.com。腾讯云的域名就是采用这种方式。
13-API风格(下):RPCAPI介绍
protoc optional
生成可以指针类型的,没用过,学习下。
1syntax = "proto3";
2
3package proto;
4option go_package = "github.com/marmotedu/gopractise-demo/protobuf/user";
5
6//go:generate protoc -I. --experimental_allow_proto3_optional --go_out=plugins=grpc:.
7
8service User {
9 rpc GetUser(GetUserRequest) returns (GetUserResponse) {}
10}
11
12message GetUserRequest {
13 string class = 1;
14 optional string username = 2;
15 optional string user_id = 3;
16}
17
18message GetUserResponse {
19 string class = 1;
20 string user_id = 2;
21 string username = 3;
22 string address = 4;
23 string sex = 5;
24 string phone = 6;
25}
1protoc --experimental_allow_proto3_optional --go_out=plugins=grpc:. user.proto
1type GetUserRequest struct {
2 state protoimpl.MessageState
3 sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
4 unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
5
6 Class string `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=class,proto3" json:"class,omitempty"`
7 Username *string `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=username,proto3,oneof" json:"username,omitempty"`
8 UserId *string `protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=user_id,json=userId,proto3,oneof" json:"user_id,omitempty"`
9}
16-代码检查:如何进行静态代码检查
goland 开发工具会帮我做一定的代码提示。
go vet 工具
https://studygolang.com/articles/9619
1package main
2
3import "sync"
4
5type B struct {
6 m sync.Mutex
7}
8
9func (b B) Lock() {
10 b.m.Lock()
11}
12
13func main() {
14 var a = B{
15 m: sync.Mutex{},
16 }
17 // 这个Lock 是会复制一份的,并不是初始化时候的锁
18 a.Lock()
19}
1go vet test1.go
2# command-line-arguments
3./test1.go:9:9: Lock passes lock by value: command-line-arguments.B contains sync.Mutex
golangci-lint
golangci-lint 聚合了几十种 go lint 工具,但默认情况仅开启如下几种:
- deadcode:查找代码中的未用代码;
- errcheck:检查代码中是否存在未处理的错误;
- gosimple:专注于发现可以进一步简化的代码的 lint 工具;
- govet:go 官方工具链中的 vet 工具;
- ineffassign:检查源码中是否存在无效赋值的情况 (赋值了,但没有使用);
- staticcheck:通用型 lint 工具,增强的 “go vet”,对代码进行很多 go vet 尚未进行的静态检查;
- structcheck:查找未使用的结构体字段;
- typecheck:像 go 编译器前端那样去解析 Go 代码并做类型检查;
- unused:检查源码中是否存在未使用的常量、变量、函数和类型;
- varcheck:检查源码中是否存在未使用的全局变量和常量;
1go install github.com/golangci/golangci-lint/cmd/golangci-lint@v1.50.1
2golangci-lint -h
3golangci-lint help linters
uber 推荐的配置
https://github.com/uber-go/guide/blob/master/.golangci.yml
1run:
2 timeout: 5m
3 modules-download-mode: readonly
4
5linters:
6 disable-all: true
7 enable:
8 - govet
9
10
11linters-settings:
12 govet:
13 # Default: false
14 disable-all: true
15 # Enable analyzers by name (in addition to default).
16 # Run `go tool vet help` to see all analyzers.
17 # Default: []
18 # 这里只开启了 printf的静态检测。
19 enable:
20 - printf
21
22issues:
23 exclude-use-default: false
24 max-issues-per-linter: 0
25 max-same-issues: 0
老师给的配置,后续需要可要参考
1run:
2 skip-dirs: # 设置要忽略的目录
3 - util
4 - .*~
5 - api/swagger/docs
6 skip-files: # 设置不需要检查的go源码文件,支持正则匹配,这里建议包括:_test.go
7 - ".*\\.my\\.go$"
8 - _test.go
9linters-settings:
10 errcheck:
11 check-type-assertions: true # 这里建议设置为true,如果确实不需要检查,可以写成`num, _ := strconv.Atoi(numStr)`
12 check-blank: false
13 gci:
14 # 将以`github.com/marmotedu/iam`开头的包放在第三方包后面
15 local-prefixes: github.com/marmotedu/iam
16 godox:
17 keywords: # 建议设置为BUG、FIXME、OPTIMIZE、HACK
18 - BUG
19 - FIXME
20 - OPTIMIZE
21 - HACK
22 goimports:
23 # 设置哪些包放在第三方包后面,可以设置多个包,逗号隔开
24 local-prefixes: github.com/marmotedu/iam
25 gomoddirectives: # 设置允许在go.mod中replace的包
26 replace-local: true
27 replace-allow-list:
28 - github.com/coreos/etcd
29 - google.golang.org/grpc
30 - github.com/marmotedu/api
31 - github.com/marmotedu/component-base
32 - github.com/marmotedu/marmotedu-sdk-go
33 gomodguard: # 下面是根据需要选择可以使用的包和版本,建议设置
34 allowed:
35 modules:
36 - gorm.io/gorm
37 - gorm.io/driver/mysql
38 - k8s.io/klog
39 domains: # List of allowed module domains
40 - google.golang.org
41 - gopkg.in
42 - golang.org
43 - github.com
44 - go.uber.org
45 blocked:
46 modules:
47 - github.com/pkg/errors:
48 recommendations:
49 - github.com/marmotedu/errors
50 reason: "`github.com/marmotedu/errors` is the log package used by marmotedu projects."
51 versions:
52 - github.com/MakeNowJust/heredoc:
53 version: "> 2.0.9"
54 reason: "use the latest version"
55 local_replace_directives: false
56 lll:
57 line-length: 240 # 这里可以设置为240,240一般是够用的
58 importas: # 设置包的alias,根据需要设置
59 jwt: github.com/appleboy/gin-jwt/v2
60 metav1: github.com/marmotedu/component-base/pkg/meta/v1
61
62linters:
63 disable-all: true
64 enable: # enable下列出 <期望的所有linters>
65 - typecheck
66 - ...
常用命令
1golangci-lint run #对当前目录及子目录下的所有Go文件进行静态代码检查:
2golangci-lint run dir1 dir2/... dir3/file1.go # 对指定的Go文件或者指定目录下的Go文件进行静态代码检查:
3golangci-lint run -c .golangci.yaml ./... # 根据指定配置文件,进行静态代码检查:
4
5# 运行指定的linter: 可以传入参数-E/--enable来使某个linter可用,也可以使用-D/--disable参数来使某个linter不可用。
6golangci-lint run --no-config --disable-all -E errcheck ./...
7# 禁止运行指定的liner:
8golangci-lint run --no-config -D godot,errcheck
代码中的特殊设置
忽略某一行所有linter的检查
1var bad_name int //nolint
忽略某一行指定linter的检查,可以指定多个linter,用逗号 , 隔开。
1var bad_name int //nolint:golint,unused
忽略某个代码块的检查。
1//nolint
2func allIssuesInThisFunctionAreExcluded() *string {
3// ...
4}
5
6//nolint:govet
7var (
8a int
9b int
10)
忽略某个文件的指定linter检查。 在package xx 上面一行添加//nolint注释。
1//nolint:unparam
2package pkg
3...
在使用nolint的过程中,有3个地方需要你注意。
首先,如果启用了nolintlint,你就需要在//nolint后面添加nolint的原因// xxxx。
其次,你使用的应该是//nolint而不是// nolint。因为根据Go的规范,需要程序读取的注释//后面不应该有空格。
最后,如果要忽略所有linter,可以用//nolint;如果要忽略某个指定的linter,可以用//nolint:
集成到goland
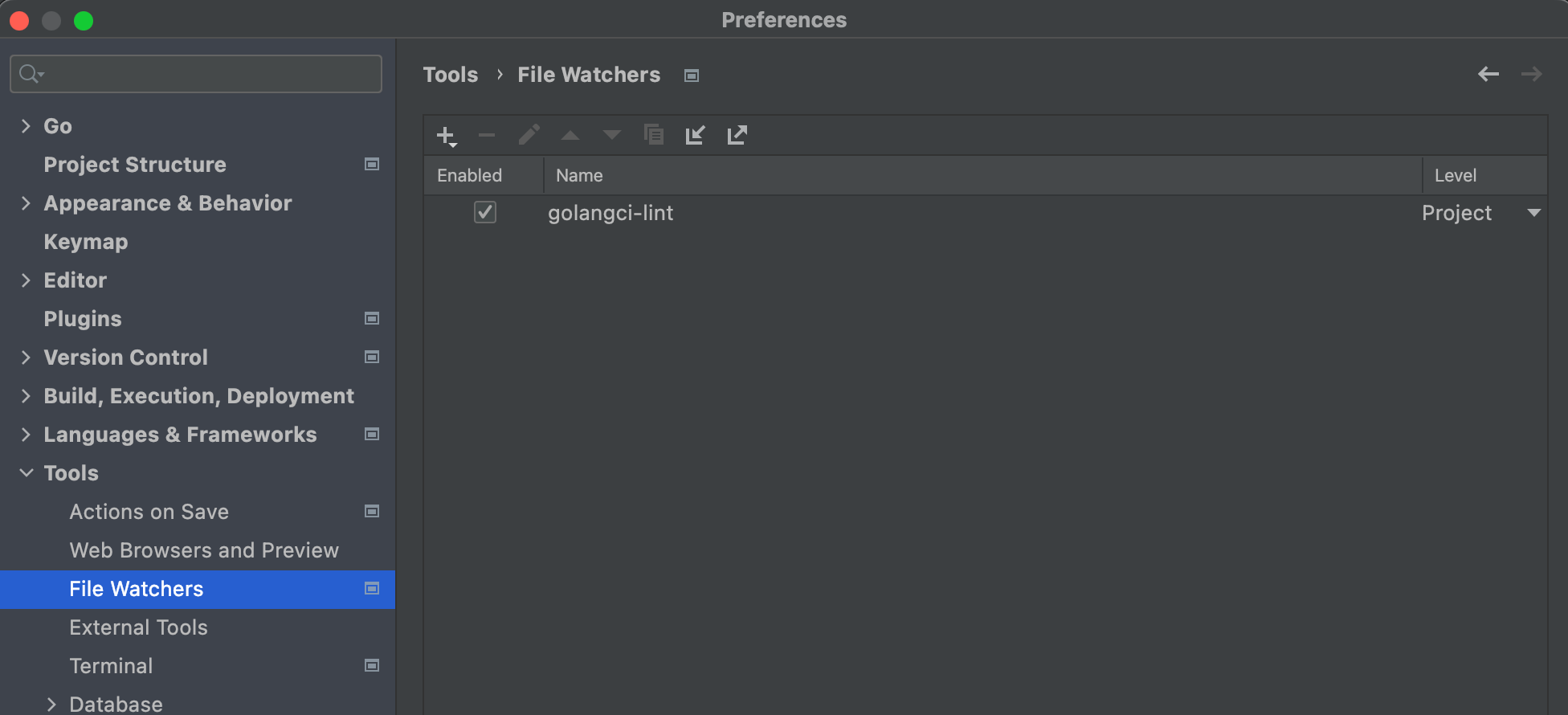
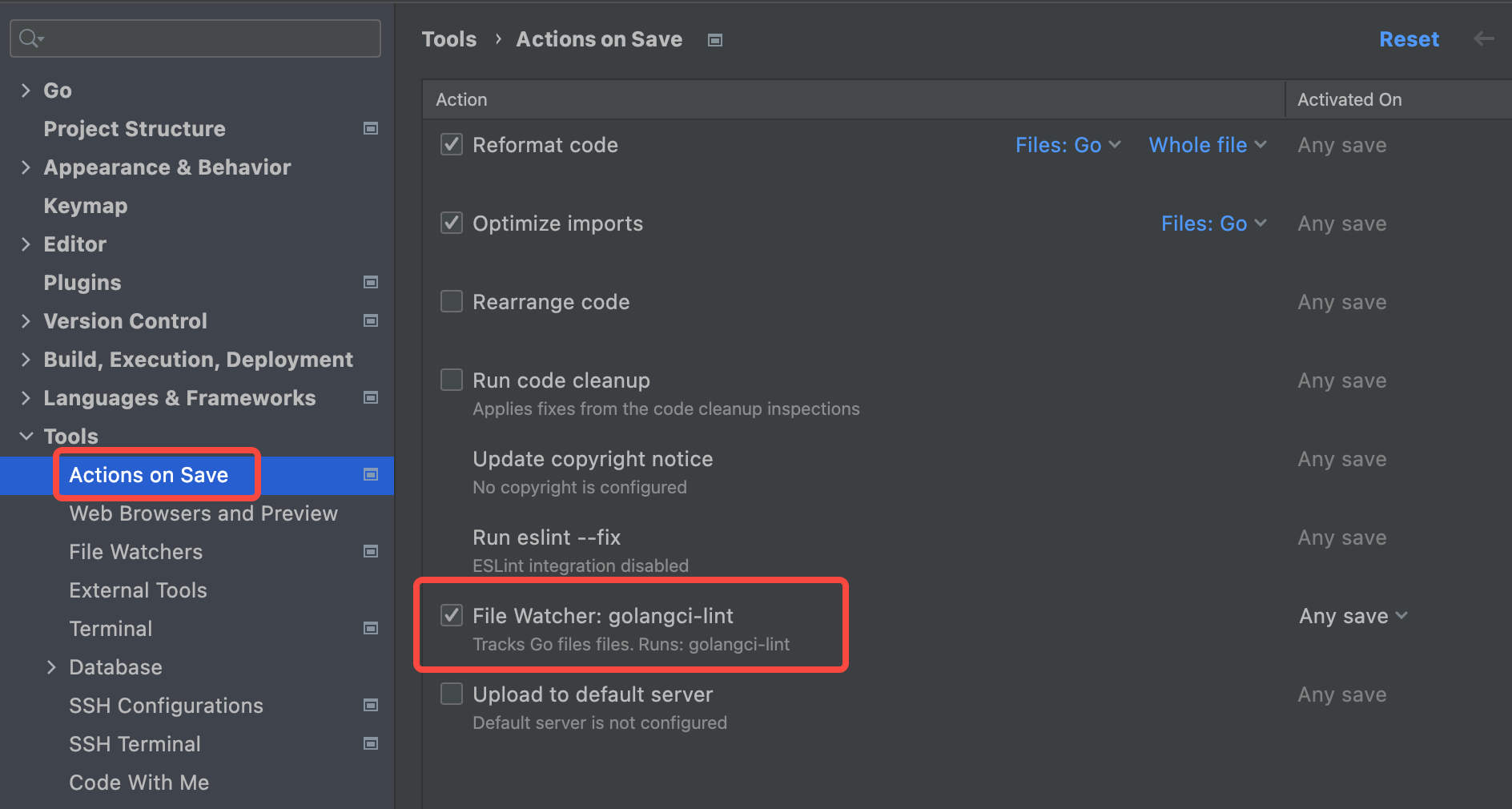
然后ctrl+s 的时候 就会进行检测,(对电脑配置要求挺高的)
18 错误码设计
项目组代号:10
服务代号:01
模块代号:0~99
错误码:0~99
| 错误标识 | 错误码 | HTTP状态码 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ErrNo | 10010000 | 200 | OK |
| ErrInternalServer | 10010001 | 500 | Internal server error (服务器内部错误) |
| ErrParams | 10010002 | 400 | Illegal params (请求参数不合法) |
| ErrAuthenticationHeader | 10010003 | 401 | Authentication header Illegal (要登录的接口,头的token认证失败,失败跳登录页面) |
| ErrAuthentication | 10010004 | 401 | Authentication failed (登录失败,输入账户、密码失败) |
| ErrNotFound | 10010005 | 404 | Route not found (请求路由找不到) |
| ErrPermission | 10010006 | 403 | Permission denied (没有权限,一些接口可能没请求权限, 这个估计暂时用不到) |
| ErrTooFast | 10010007 | 429 | Too Many Requests (用户在给定的时间内发送了太多请求) |
| ErrTimeout | 10010008 | 504 | Server response timeout (go服务这边不会返回,一般是nginx、网关超时 才返回504) |
| ErrMysqlServer | 10010101 | 500 | Mysql server error (mysql 服务错误) |
| ErrMysqlSQL | 10010102 | 500 | Illegal SQL (sql 代码错误) |
| ErrRedisServer | 10010201 | 500 | Redis server error (redis 服务错误) |
http code标志错误,非200, 客户端再根据 错误码进行对应的处理
以在自己的框架中实现, 也是参考了这个 。
https://github.com/cr-mao/gosky/blob/main/docs/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8api.md
https://github.com/cr-mao/gosky/blob/main/infra/errcode/errcode.go
19.如何设计错误包
直接看实现。 已经基本掌握了它的用法, 并变成了自己的包,并丰富了readme文档,和test代码。
https://github.com/cr-mao/errors
微服务该采用Multi-repo 还是 Mono-repo ?
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2064077
Mono-repo 和 Multi-repo 同样流行,哪一个更好取决于你的项目大小、项目需求以及你需要的版本控制和访问控制级别。
Mono-repo 侧重一致性,而 Multi-repo 侧重于解耦。在 Mono-repo 中,整个团队可以看到某一个人完成的更改,而 multi-repo 为每个团队创建一个单独的 repo,这些团队只能访问所需的仓库。如果你想为你的项目使用 mono-repo 和 multi-repo 的组合,你可以使用 meta,一个管理多个项目和库的工具。