locust+boomer
locust 是 开源负载测试工具。使用 Python 代码定义用户行为,也可以仿真百万个用户https://www.locust.io/
locust架构图如下:

locust 部署
master 采用 python,slave 我们用go 来写。
我们直接使用docker就行了
https://hub.docker.com/r/locustio/locust
下载镜像: docker pull locustio/locust:1.6.0
docker启动 看文档 https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/running-in-docker.html#running-in-docker
locustfile.py 内容如下:
1#coding: utf8
2from locust import User, task
3
4class Dummy(User):
5 @task(20)
6 def hello(self):
7 pass
注意必须是locustio/locust必须是1.6.0 ,不然连上了,也会报不是no slave
1#docker run -p 8089:8089 -v $PWD:/mnt/locust locustio/locust -f /mnt/locust/locustfile.py
2
3docker run -d --name locust \
4-p 8089:8089 \
5-p 5557:5557 \
6-v /Users/mac/code/locust/master:/app \
7-w /app \
8locustio/locust:1.6.0 \
9-f /app/locustfile.py --master -H http://0.0.0.0:8089
10
11# host 模式跑不起来。
pip安装
1 pip3 install locust==1.6.0
2 # 我本地有点问题,那么就用docker吧。
-
Number of users to simulate:设置模拟的用户总数
-
Hatch rate (users spawned/second):每秒启动的虚拟用户数
-
Start swarming:执行locust脚本
用boomer编写slave 代码
代码如下
1package main
2
3import "time"
4import "github.com/myzhan/boomer"
5
6func foo() {
7 start := time.Now()
8 time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
9 elapsed := time.Since(start)
10
11 /*
12 Report your test result as a success, if you write it in locust, it will looks like this
13 events.request_success.fire(request_type="http", name="foo", response_time=100, response_length=10)
14 */
15 boomer.RecordSuccess("http", "foo", elapsed.Nanoseconds()/int64(time.Millisecond), int64(10))
16}
17
18func bar() {
19 start := time.Now()
20 time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
21 elapsed := time.Since(start)
22
23 /*
24 Report your test result as a failure, if you write it in locust, it will looks like this
25 events.request_failure.fire(request_type="udp", name="bar", response_time=100, exception=Exception("udp error"))
26 */
27 boomer.RecordFailure("udp", "bar", elapsed.Nanoseconds()/int64(time.Millisecond), "udp error")
28}
29
30func main() {
31 task1 := &boomer.Task{
32 Name: "foo",
33 // The weight is used to distribute goroutines over multiple tasks.
34 Weight: 10,
35 Fn: foo,
36 }
37
38 task2 := &boomer.Task{
39 Name: "bar",
40 Weight: 20,
41 Fn: bar,
42 }
43
44 boomer.Run(task1, task2)
45}
1go run main.go --master-host=127.0.0.1 --master-port=5557
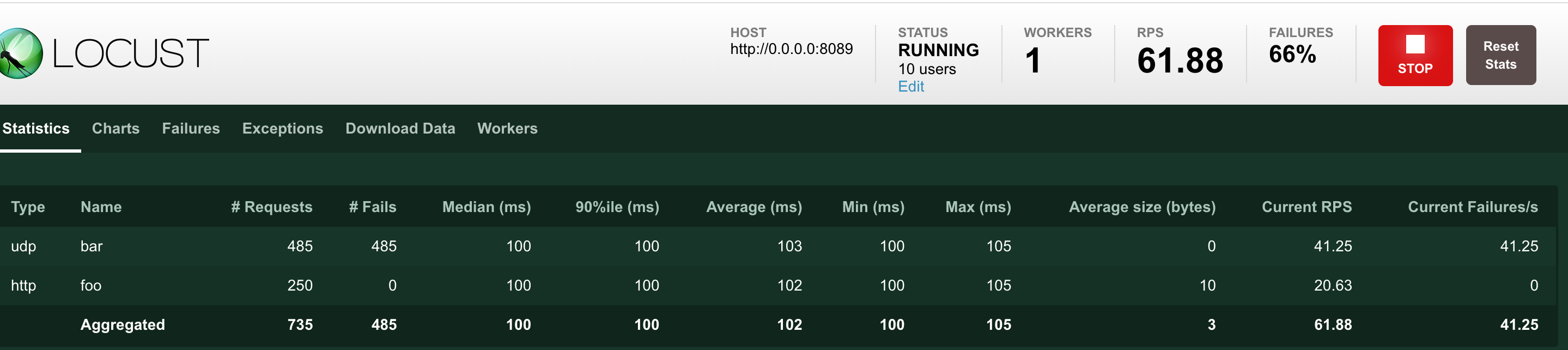
- Type:请求类型,即接口的请求方法;
- Name:请求路径;
- requests:当前已完成的请求数量;
- fails:当前失败的数量;
- Median:响应时间的中间值,即50%的响应时间在这个数值范围内,单位为毫秒;
- Average:平均响应时间,单位为毫秒;
- Min:最小响应时间,单位为毫秒;
- Max:最大响应时间,单位为毫秒;
- Content Size:所有请求的数据量,单位为字节;
- reqs/sec:每秒钟处理请求的数量,即QPS;
gin+gorm 实战压测
主要是为了知道机器大概能抗多少并发,连接数应该怎么设置
web代码
1package main
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
6 "github.com/jinzhu/gorm"
7 _ "github.com/jinzhu/gorm/dialects/mysql"
8 "log"
9 "sync"
10)
11
12type Book struct {
13 Id int `gorm:"column:id;AUTO_INCREMENT;PRIMARY_KEY"`
14 BookName string `gorm:"column:book_name;type:varchar(255)" json:"book_name,omitempty"`
15}
16
17var db *gorm.DB
18var dbonce sync.Once
19
20func getDB() *gorm.DB {
21 dbonce.Do(func() {
22 var err error
23 db, err = gorm.Open("mysql",
24 "root:root@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/blog?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local")
25 if err != nil {
26 log.Fatal(err)
27 }
28 db.SingularTable(true)
29 db.DB().SetMaxIdleConns(50)
30 db.DB().SetMaxOpenConns(500)
31 })
32 return db
33}
34
35var reqNum int
36
37func main() {
38 r := gin.New()
39 gin.SetMode("debug")
40 r.Handle("GET", "/", func(context *gin.Context) {
41 context.JSON(200, gin.H{"message": "index"})
42 })
43 r.Handle("GET", "/prods", func(context *gin.Context) {
44 books := []Book{}
45 getDB().Table("cr_books").Order("id desc ").Limit(10).Find(&books)
46 context.JSON(200, books)
47 reqNum++
48 fmt.Println(reqNum)
49 })
50 r.Run(":8080")
51
52}
boomer代码
1package main
2
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "github.com/myzhan/boomer"
6 "net/http"
7 "time"
8)
9
10func reqWeb(name string, url string) {
11 start := time.Now()
12 rsp, err := http.Get(url)
13 if err != nil {
14 boomer.RecordFailure("http", name, 0,
15 fmt.Sprintf("request err:%s", err.Error()))
16 return
17 }
18 defer rsp.Body.Close()
19 end := time.Since(start)
20 if rsp.StatusCode >= 400 {
21 fmt.Println(rsp.StatusCode)
22 boomer.RecordFailure("http", name, end.Nanoseconds()/int64(time.Millisecond),
23 fmt.Sprintf("status code:%d", rsp.StatusCode))
24 } else {
25 boomer.RecordSuccess("http", name,
26 end.Nanoseconds()/int64(time.Millisecond), rsp.ContentLength)
27 }
28}
29func main() {
30 //index := &boomer.Task{
31 // Name: "myweb",
32 // Weight: 1,
33 // Fn: func() {
34 // reqWeb("index_page", "http://127.0.0.1:8080")
35 // },
36 //}
37 prods := &boomer.Task{
38 Name: "myweb",
39 Weight: 1,
40 Fn: func() {
41 reqWeb("prods_page", "http://127.0.0.1:8080/prods")
42 },
43 }
44 //boomer.Run(index, prods)
45 boomer.Run(prods)
46}
1go run main1.go --master-host=127.0.0.1 --max-rps=400 # 最多400rps
主要要加max-rps参数,不然请求数非常😱
我的电脑15年mac pro
Locust 设置1个用户1个进行测试。设置450rps,几乎没有错误。连接池设置500最大连接数50空闲数,请求8万多次没有一条异常
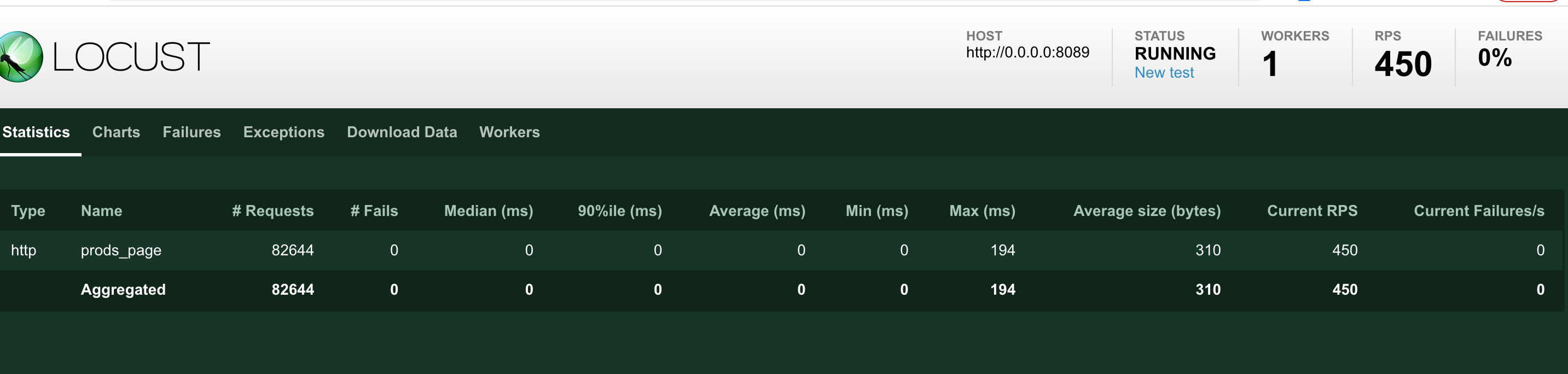
但是设置460rps 的时候 就开始出现异常了,所以总结。代码的连接池设置还是需要尽量设置大点的。
进行100个用户测试。 连接池设置500最大连接数50空闲数, rps设置449,基本达到用户40个左右就开始出现异常。
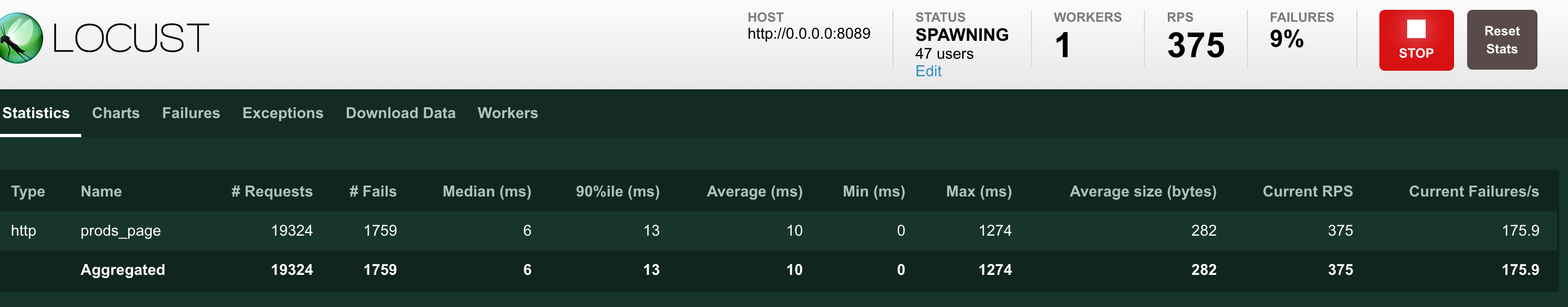
100个用户, 连接池设置500最大连接数50空闲数,rps设置400, 没有异常
100个用户, 连接池设置500最大连接数50空闲数,rps设置449, 有异常 (总结连接数要大于 并发请求数会好点)
wrk
开源的性能测试工具 wrk, 很类似apache benchmark(ab)同属于性能测试工具,但是比 ab 功能更加强大,并且可以支持lua脚本来创建复杂的测试场景。
安装
可以自己编译安装, 也可以用第三方的镜像
https://hub.docker.com/r/williamyeh/wrk
1docker pull williamyeh/wrk
使用
使用12个线程并保持400个HTTP连接打开的状态下运行5秒的基准测试
1docker run --rm \
2williamyeh/wrk \
3 -t12 -c400 -d5s --latency http://192.168.29.1:8080/user/123
4#
wrk支持在三个阶段对压测进行个性化修改,分别是
1、启动 阶段 : function setup(thread) 线程已初始化但没启动的时候调用
2、结束阶段 function done(summary, latency, requests)
- 运行阶段
- function init(args)进入运行阶段时,调用一次
- function delay()每次发送request之前调用
- function request()生成请求;每一次请求都会调用该方法
- function response(status, headers, body)在每次收到一个响应时调用
用lua脚本进行动态请求
function wrk.format(method, path, headers, body)
根据参数 ,生成一个HTTP rquest
user.lua
1request = function()
2 local uid = math.random(1, 1000)
3 local path = "/user/".. uid
4 return wrk.format("GET", path)
5end
1docker run --rm \
2-v `pwd`:/data \
3-w /data \
4williamyeh/wrk \
5 -t12 -c400 -d5s --latency http://192.168.29.1:8080 -s user.lua